Chapter four notes
Newtons Third law
When we were dealing with balanced an unbalanced forces we were looking at the forces that were acting on one object. For example when an old tire is hanging from a tree what are the forces acting on the tire? Gravity down on the tire and the rope up on the tire. Notice how both forces are acting on one object. If they are equal there is either dynamic or static equilibrium. If they are unequal then there is an acceleration which is caused by the unbalanced forces.
In chapter four we are going to look at force interactions. This is know as Newton's third law: Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts and equal and opposite force on the first.
This can be condensed to say for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
If I stand and push against the wall, the wall pushes against me. The action force would be me on the wall and the reaction force would be the wall on me. REMEMBER THIS IS A SINGLE INTERACTION between the wall and me.
To be an action-reaction pair two rules must apply.
rule one: You need equal and opposite forces.
rule two: You need two different objects.

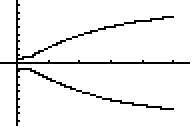
Look at the graph above. This is a Force vs. time graph for two force probes that are connected together and pulled in opposite directions. Which hand pulled harder? b.) which hand was stationary? Can you tell? Why or why not. What is true about the tension in the string compared to the pull? For example if I pull with 10 N what is the tension in the string? How much is the other scale pulling with?
karate demonstration: Remember to break a piece of wood you need to apply a large force. Since the mass of my hand is constant to generate a large force I need to generate a large acceleration. (Newton's second law F=ma). If you do not have a large enough acceleration then you will not generate enough force to break the wood. Also according to Newton's third law for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. My hand on the wood is the action force and the wood on my hand is the reaction force. Therefore I want to be careful to use the "fleshy" part of my hand to make the contact less painful. Finally since the interaction time involving the wood and my hand is short there is very little pain.
Lets take a look at when you have Newton' 3rd law forces and balanced and unbalanced forces acting in the same situation.
A person pushes on a heavy box and accelerates it across the room. What are the action reaction forces?
1.) Action force = person on the box
2.) Reaction force = box on the person.
Notice for Newton 3rd law forces we have two objects and two forces.
If these two forces are equal, then why does the box move? To answer this question, you need to look at the forces that ONLY act on the BOX. These are not action reaction, but net forces which we have worked on before.
On the box you have
1.) you pushing on the box
2.) Friction pushing against the box
If you can apply more force than the friction they you will be able to accelerate the box. Notice for net forces we are dealing with multiple forces acting on ONE object. Look at this demonstration done in class. Identify the action and reaction forces. Also, be able to explain why the person moves forward.
Look at this video of the Ethanol Pringles cannon
a.) What has a larger acceleration the lid or the
can? Explain why.
b.) Identify a Newton force pair for this
c.) Explain in detail why the car moves.
Action reaction for gravity:
If the action force is the earth on you then the reaction force
is you for the earth. Remember the law for gravity= (Gm1m2)/d2
The force of gravity is directly proportional to the masses of the object
and inversely proportional to the SQUARE of the distance between them
Remember: Since action-reaction forces act on different objects they cannot cancel each other out. Balanced and unbalanced forces act on the same object so they can cancel each other out.
Look at this video of a tug a war between
the girls and the boys. (remember they boys only have their socks on)
a.) who is pulling harder on the rope, the boys or the girls?
b.) Why were the girls able to win? (with shoes on they were able to generate
more frictional force against the ground)
Action and reaction forces on objects with different masses.
Most of you are familiar with how a rifle works. When the bullet it is fired what are the action and reaction forces?
1. Action force = bullet on rifle
2.) reaction force = rifle on bullet.
Question: Which has the larger acceleration? The bullet of course. How can it have a larger acceleration if the same force is applied? Remember Newton's second law acc = F/m Since the bullet has a much smaller mass it undergoes a much greater acceleration. Remember the bullet only accelerates why it is in the gun barrel. Once it leaves the gun barrel it immediately starts to slow down and then gravity pulls it downward.
Here is a video of a girl on a skateboard pulling on a string
a.) if the action force is the girl on the string, what is the
reaction force? (string on girl)
b.) if those two forces are equal and opposite then why is the girl able to
move?
Here is a video of a boy and a girl on a skateboard pulling on a string and a video of two girls on skateboards pulling on a string.
a.) Who is pulling harder, the boy or the girl?
b.) Watch the motion of the boy compared to the girl. Why the difference?
c.) Watch the motion of the two girls on the skateboard. Why is their motion
different from the boy and girl on the skateboard?
Here is a video of two girls back to back on some skateboards and one girl pushes on the other girl
a.) identify the action and reaction force
b.) Explain why each girl moves and what is responsible for their movement.
CAR ON BOARD AND FAN ON SKATEBOARD VIDEO
1.) If I hold the car still what will happen? Explain why
2.) If I hold the board still, what will happen and why?
3.) If I don't hold either, what will happen and why?
FAN OF SKATEBOARD
1.) Here is a regular fan on a skateboard. Identify the action reaction (air on fan and fan on air) and be able to explain why the fan moves. (force of air on fan is greater than the force of friction on the wheels of the skateboard
2.) Here is a fan with a sail on it. Will it move? Why or why not?
3.) Here is the same fan with the sail down. Will it move? Why or why not?
Remember to have motion on an object it must have an EXTERNAL force applied on it.
Here is the video of the single person catching and throwing the ball while on the skateboard. Notice that they can move back when they catch or throw the ball. What is the action-reaction forces? (ball on hand and hand on ball) Why does the person move? (Force of ball on them is greater than the force of friction between the wheels and the ground)
Here is the second situation of two people on a single cart. If they throw the ball back and forth with they be able to move like the single person? Why or why not? (They cannot because their is not an external force being applied. They are all part of the same system so they are INTERNAL FORCES which cannot cause a change in the motion of the object.